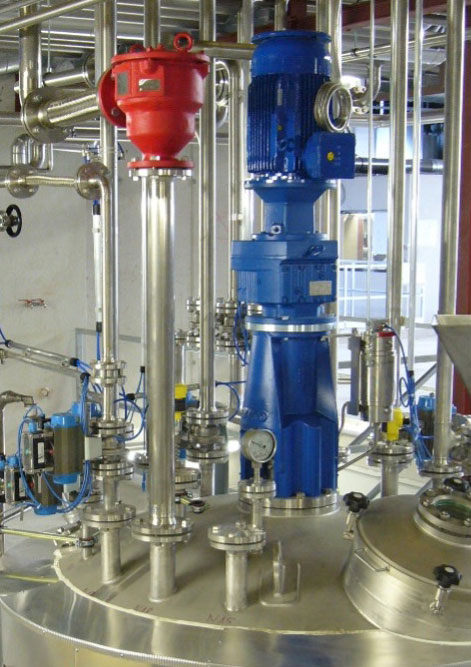
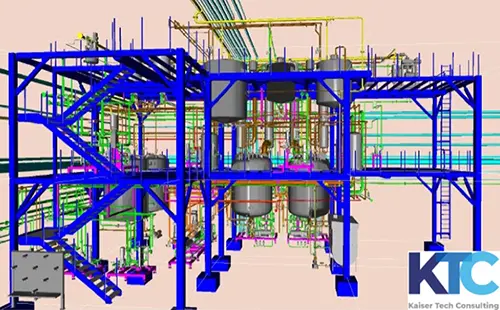
Engineering and construction of high-performance synthetic resin plants – efficient, safe and flexible
Planning and construction of synthetic resin plants
Calling up the greatest possible capacity and flexibility of plant technology – with maximum safety and product quality. These projects are realized with reliable, creative and professional planning and implementation through over 25 years of experience in synthetic resin plant engineering.
The industrial production of different synthetic resin types requires greatest knowledge in the field of
- dosing of raw materials
- heating and cooling of technical equipment
- construction and connection plant technology
- Design and construction of the apparatus
- material selection of the apparatuses, valves and instruments
- Automatic control of synthetic resin plants
The best possible results in terms of yield, quality and safety can only be achieved if the plant design is ideally adapted to the synthetic resin type and application.
Alkyd resin plants/polyester resin plants
Due to the continuous development of alkyd resins and polyester resins according to the requirements of industry and trade as well as strict requirements from environmental protection, alkyd resins and polyester resins continue to play an important role and are still among the most important synthetic resins.
Alkyd resin plants and polyester resin plants specially tailored to industrial production considering the thermal stresses in production, the material requirements for equipment, fittings and instruments, the optimized separation of alcohols and water in polyester resin production and an optimized safety philosophy by combination of classic, mechanical safety technology with high sophisticated, safety-oriented and fully automatic control systems.
Applications of Polyester resin/alkyd resin:
Alkyd resins:
formulation of coatings, e.g. wood coatings, painters’ lacquers as well as parquet sealers, glazes, maintenance systems, primers, top coats and one-coat paints, stoving paints, 2K paints and printing inks (mainly pasty).
Polyester resins:
Casting resins for the embedding of electrical and electronic components; laminates for the automotive industry, container industry, building industry, furniture industry, toolmaking; molding compounds in electrical engineering and precision engineering/ mechatronics; binders for paints and coatings.
Acrylic resin plants
Acrylic resins are characterized by their excellent physical properties, such as
- transparency, glossy appearance and color stability
- resistance to weather, chemicals, heat and solvents
- Processability, elasticity, excellent mechanical strength
- Fast drying and pigment dispersion at room temperature
in a wide variety of applications.
In the production of acrylic resins, the special properties of the chemical reaction must be considered in specially designed acrylic resin plants. The exothermic nature of the reaction must be controlled and the plant operators, the environment and the plant equipment must be safely protected. Safe elimination of the resulting energy through condensation systems, classical and mechanical protection devices together with inherent-safety, fully automatic control systems ensure optimized protection, highest yield and maximum quality during production in acrylic resin plants. Continuous metering of raw materials also enables the amount of energy to be controlled and safe production to be achieved with minimum batch time.
Electropolished surfaces, optimized stirring systems not only ensure optimal heat transfer, but also low-residue production.
Applications for acrylic resins:
Production of paints and varnishes due to their excellent durability and adhesion to various substrates. For wood, decorative and industrial coatings, building protection and road markings,
for the formulation of primers, finishing paints and coatings, automotive
as compounds for injection or compression molding, for printing inks and as adhesives
as waterborne latex emulsions.
Phenolic Resin Plants
The first phenolic resin developed by Leo Hendrik Baekeland in 1905 is considered to be the first completely synthetically produced plastic material in the world. Since then, development has progressed continuously due to ever new technical requirements and for environmental reasons. Phenolic resins (PF resins/phenoplastics) are a condensation product of phenol and formaldehyde and are extremely heat-resistant, easy to press, with excellent dimensional stability and insulating properties.
For production in phenolic resin plants designed specifically for this purpose, it is important to control the reaction – either in a one-pot process or in continuous, stoichiometric metering of all solid and liquid reactants. Heated by steam or hot water, it is most important to ensure optimum utilization of the heating and cooling surfaces, optimum and fast heat distribution in the reactor, and adequate dimensioning of the plant components.
Applications for phenolic resins:
Molding compounds for presses, transfer molding and injection molding, adhesives, paint and impregnation purposes, flooring, curing agents for press compounds, production of printed circuit boards, heat-resistant and robust components, e.g. brake linings, foams or hard fiber boards.
Production and coating of laminates with very high resistance, for which phenolic resins are added to the wood panels, paper or fabric webs as powerful binders.
Urea-Formaldehyde resin plants /Melamine resin plants
The condensation of urea-/ or and melamine with formaldehyde leads to urea formaldehyde resins (UF-resin) or melamine resins (MF resins), the aminoplastics family, which form thermosetting plastics after curing. In addition to the classic resins, melamine-phenol-formaldehyde resins (MPF resins) and melamine-urea resins (UMF resins) are also produced by modifying the reaction partners. Melamine resin plants need to be designed in maximum flexible condition to produce all required resins with one configuration.
UF-/MF resins generally have good weathering and light resistance and durable thermal/mechanical stability.
Urea Formaldehyde resin plants (UF resin plants) and Melamine resin plants (MF resin plants) are tuned for moderate heating with steam or hot water and cooling with the largest possible exchange surface. The necessary dosing of acids and alkalis is fully automatic, at best in coordination with inline analytic methods for end-point detection of the reaction.
Applications for UF/MF/UMF/PF resins:
Laminates with paper, glass fibers or cotton fabric, production of moldings for electrical insulating parts, precondensates are used as glue or varnish resins, production of laminates, tableware, household appliances and furniture.
Varnish production plants (plants for printing inks binders)
Varnishes are used as binders for printing inks for letterpress and offset printing. They are produced by mixing resins and vegetable or mineral oils. The resins used are mainly phenol-modified rosin resins.
During the actual mixing process, the colloidally dissolved resins absorb the oil and swell to form a viscous mass. The mechanical, physical and chemical properties of the actual printing ink are determined by the varnishes.
Production in specially designed varnish plants takes place at high temperatures usually above 200°C, so the plants together with the accessories are heated with thermal oil. One peculiarity of the production process is the high proportion of solids in the exhaust air, which is freed of solids by specially flushed exhaust ducts.
For more information, please contact me at any time!